
With the publication of Satoshi Nakamoto’s white paper in 2008, the concept of blockchain emerged as the public transaction ledger for bitcoin, the world’s first decentralized cryptocurrency. Since then, the two entities have remained inextricably linked, with bitcoin soaring in value and popularity and blockchain rising in hype and enterprise viability.
Today, despite the inherent link between the two, blockchain and bitcoin have drifted in different directions in terms of both connotation and definition. Here are some of the key technical differences between the two:
Blockchain | Bitcoin |
| Distributed ledger platform | Digital currency built on top of blockchain |
| Broad scope with hundreds of use cases | Limited in scope to financial markets & payments |
| Simplifies complex technology ecosystems to run on a decentralized single platform | Simplifies payments to be faster and not rely on a central authority (e.g. bank) |
| Public, private and consortia-based blockchains transmit and store data on any business process | Largely limited to the ledger of data on financial transactions |
| Useful in data transactions between multiple parties (i.e. logistics provider, insurer and retailer with supply chain data all on one blockchain) | Used mainly for peer-to-peer financial transactions (e.g. payments) |
| Access is permissioned and transparent so parties can see who makes transactions and views data | Parties often prefer to remain anonymous |
| Mining is optional to make the blockchain work, and a consensus protocol can be implemented without relying on miners to verify each transaction | Mining is key to making this approach work with miners proving accuracy of bitcoin transactions, adding “blocks” to the “chain” of existing verified transactions |
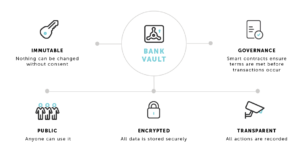
WHAT IS BLOCKCHAIN? THE BANK VAULT ANALOGY
Blockchain is defined as a technology for decentralized payments and data management that allows digital information (the block) to be stored and distributed in a public database (the chain) that’s validated by a wider community rather than a central authority. To understand how blockchain works, it’s helpful to think of the broadly used bank vault and its benefits:
In this analogy, the blockchain works similarly to a bank vault to keep valuable information secure yet transparent, publicly accessible yet immutable. Only parties with permission to enter the vault – or manipulate the blockchain – can make changes to the data, and these changes are governed by and visible to the other parties operating the vault/blockchain.
BLOCKCHAIN’S RISING ENTERPRISE VIABILITY
In recent years, enterprises have started to explore various new use cases for blockchain that go beyond bitcoin. Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology’s powerful features like immutability, encryption and transparency make blockchain the perfect platform for various data-rich business processes.
Moving forward, enterprises are seeking to unlock the benefits of blockchain in many key areas, including supply chain, data management, audit trails, governance, regulatory compliance and more. Overall, when implemented into production, blockchain has the potential streamline and, in some instances, automate the above processes. Blockchain offers the following opportunities for businesses:
- Increase operational efficiency by storing and accessing data on a single digital ledger
- Save time and money by cutting out middlemen
- Build trust through enhanced security, transparency and encryption
- Improve traceability in the supply chain (e.g. SigmaLedger)
- Unlock new business models through digitization (e.g. tokenization, digital identity, smart contracts, ownership rights)
KEY BLOCKCHAIN USE CASES BEYOND BITCOIN & PAYMENTS
While blockchain will undoubtedly continue to be used as the foundation for cryptocurrency and other forms of alternative payments, its hundreds of other use cases make it a powerful underlying technology that could provide cost savings and unlock significant efficiencies not offered by other solutions.
- Blockchain in Life Sciences
- Drug Traceability
- Counterfeit Drug Prevention
- Blockchain in Healthcare
- Provider Data Management
- Coordination of Benefits
- Patient Consent Management
- Blockchain in Transportation & Logistics
- Luggage & Cargo Traceability
- Vehicle Management
- Global Trade
- Blockchain in Agriculture
- Traceability
- Compliance & Quality Control
- Inventory Management
Investing in Blockchain
Currencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, have garnered much attention and excitement, but investing in them is challenging, time-consuming and entails significant volatility.
Blockchain is the record-keeping technology behind cryptocurrency. Unlike the use of cryptocurrencies as a standalone investment, the broader blockchain technology entails less volatility and provides investors a more streamlined exposure to cryptocurrency and other emerging blockchain uses.
The ‘Demand Blockchain’ portfolio is designed as a comprehensive investment solution. It has exposure to over 50 companies that are actively involved in the development and utilization of blockchain technologies. Although a significant portion is allocated to the blockchain industry, we ensure that your portfolio is also globally diversified, which reduces volatility in the event of blockchain sector underperformance.
Are you interested in investing in the evolution of blockchain technology as part of a diversified investment strategy? If so, we are here to help! Open an account here or schedule a Zoom conference with one of our advisors today.
This report is a publication of Demand Wealth. Information presented is believed to be factual and up-to-date, but we do not guarantee its accuracy and it should not be regarded as a complete analysis of the subjects discussed. All expressions of opinion reflect the judgment of the author as of the date of publication and are subject to change.
